Overview
FP MAP, comprising an amphoteric polymer, has hydrophobic and hydrophilic sides in its chemical structure. The hydrophobic side binds to the non-specific protein binding sites on the solid substrate, while the hydrophilic side is exposed to the environment to build a protective hydrophilic layer that prevents the binding of interfering proteins.
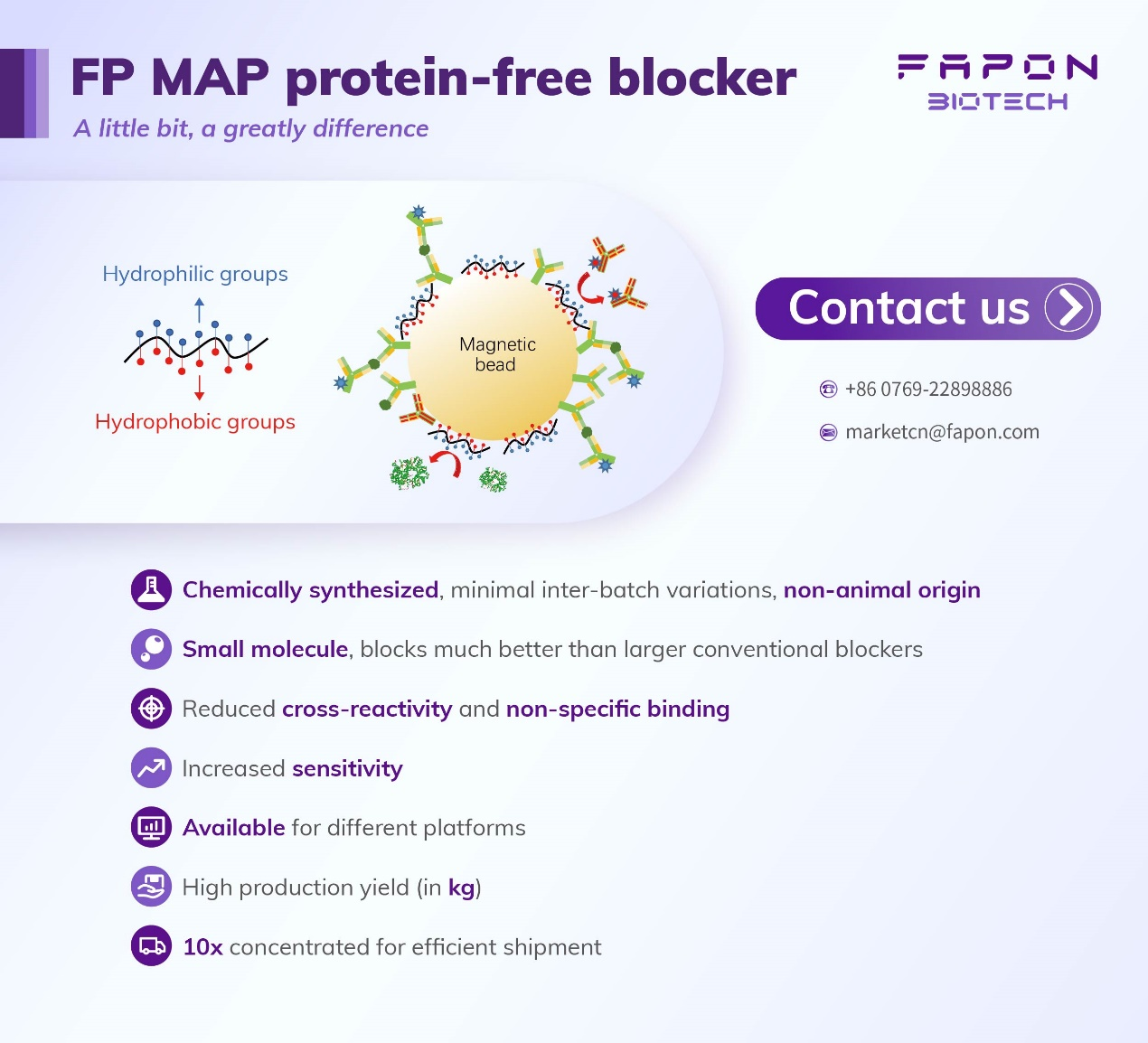
Structure and blocking mechanism
FP MAP, being much smaller than conventional blockers such as bovine serum albumins (BSAs), covers more effective area and blocks a larger surface area.
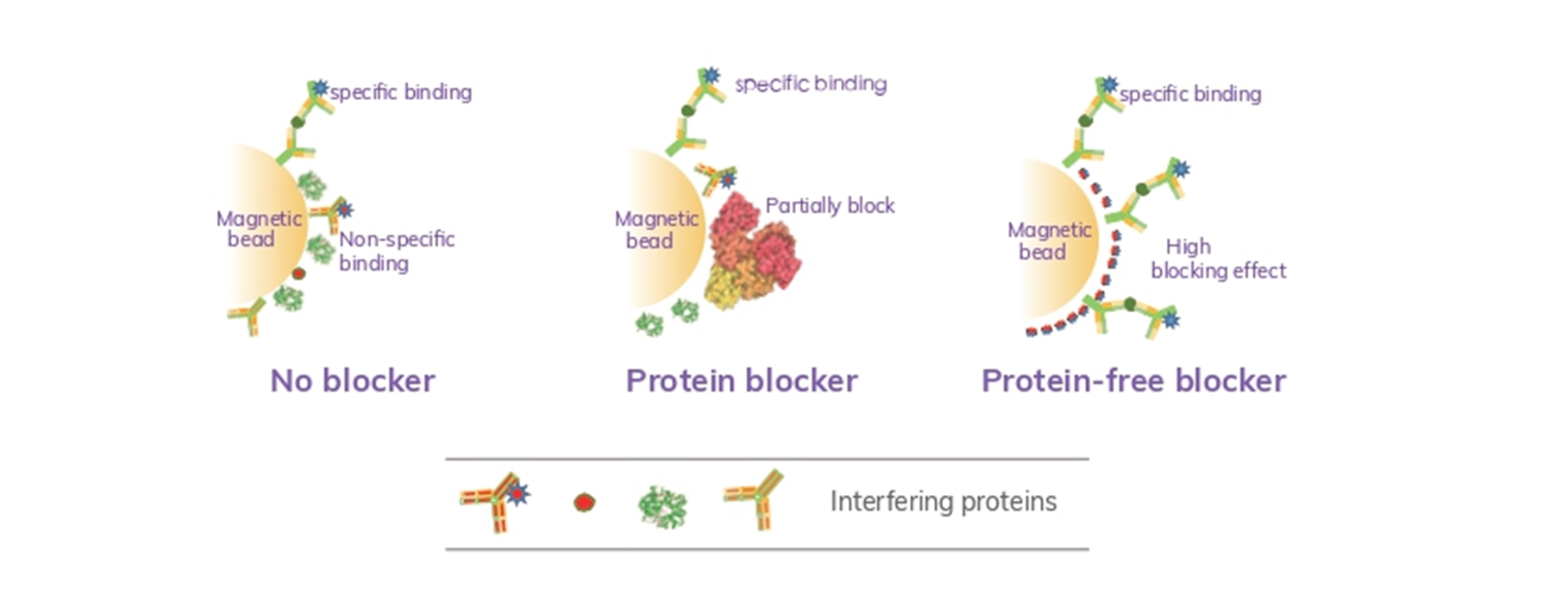
Performance
Non-specific binding test
FP MAP's performance verified on the ELISA platform:
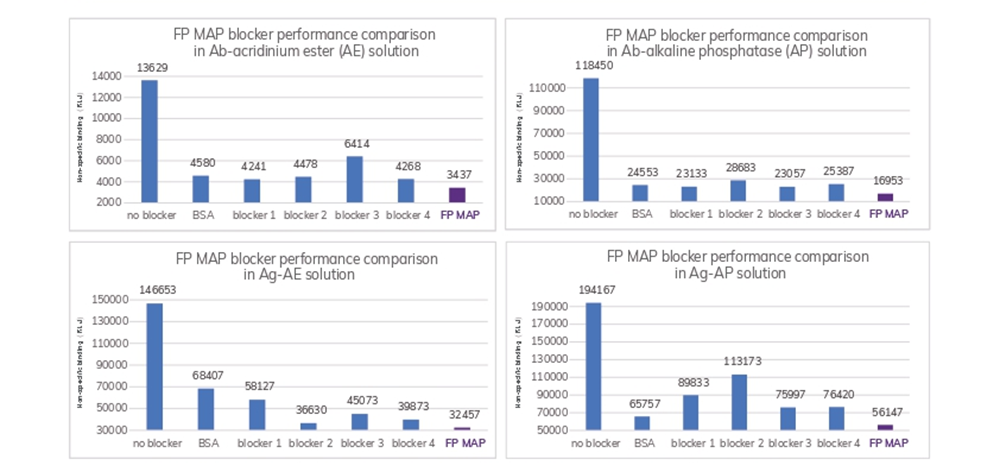
FP MAP demonstrated superior inhibiting effect of non-specific binding on the ELISA platform.
FP MAP's performance verified on the CLIA platform:
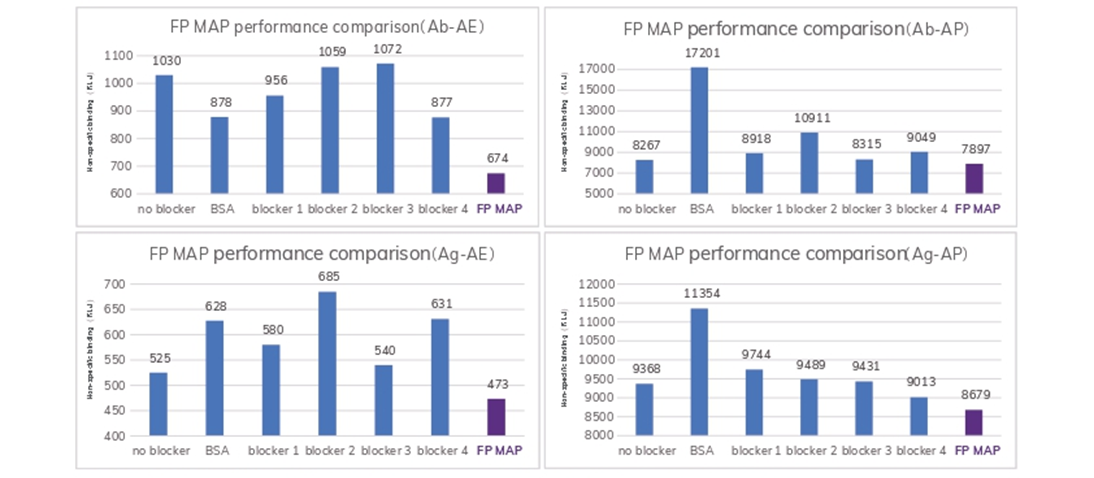
FP MAP demonstrated the superior inhibiting effect of non-specific binding on the CLIA platform.
Sensitivity test
FP MAP as a blocker for magnetic beads
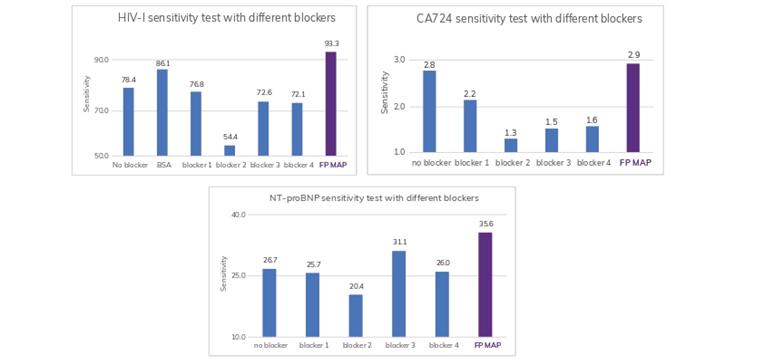
FP MAP demonstrated superior sensitivity than other commercial blockers.
FP MAP as a blocking additive in magnetic bead solution or AE solution
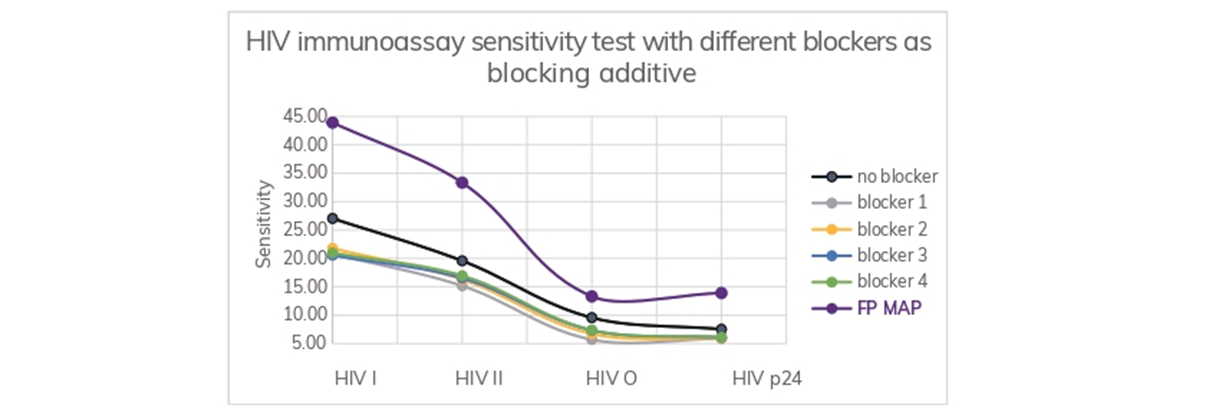
FP MAP increased the sensitivity of the immunoassay for HIV more than other commercial blockers did.
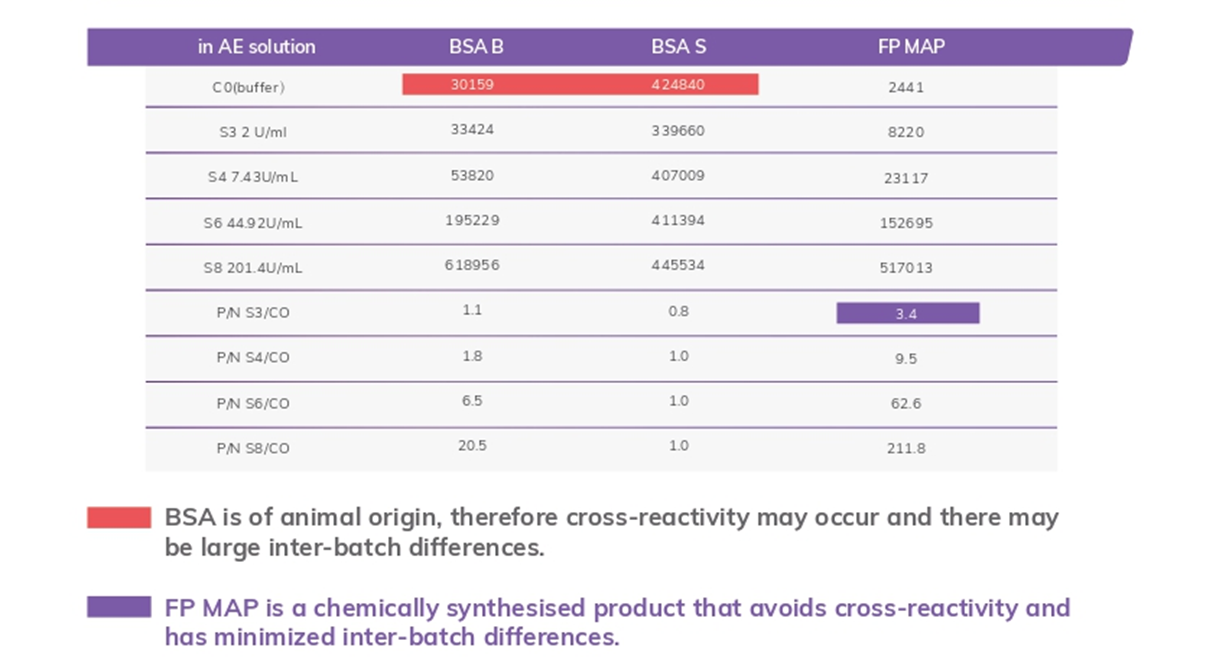
Avoiding cross-reactivity
FP MAP as a blocking additive in bead solution or AE solution
Stability test
FP MAP is added as a blocking additive in AE, magnetic bead solution, or both of the above. The reagents are heated at 37°C for 7 days, RLUs are measured and compared to the control without FP MAP and the deviations are calculated.
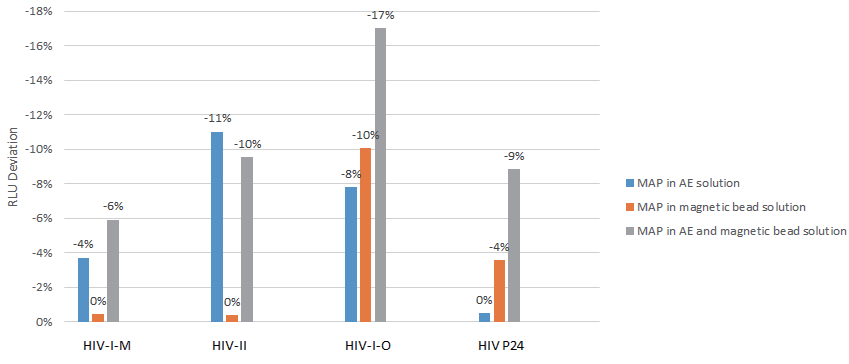
FP MAP as a blocking addtive in solutions does not affect the reagent stability.
Join us for a better future of IVD.
If you have any question or need any support, please fill out the information below.






