A Femtogram-Scale Breakthrough in hs-cTnI Assays
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are a group of chronic diseases of the heart and blood vessels. Statistics from the World Health Organization showed that an estimated 17.9 million people died from CVDs in 2019, representing 32% of all global deaths [1]. The American Heart Association reported in 2022 that over 20 million people died from CVDs in 2021 [2]. Coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction and heart failure are among the heaviest burden of CVDs. In China, the number of deaths from CVDs increased from 3.09 million in 2005 to 4.58 million in 2020, demonstrating a rising trend.
Cardiac troponin I (cTnI) is significant for rapid diagnosis, monitoring, treatment and prognosis evaluation of myocardial infarction and myocardial injury. It is the primary biomarker for myocardial infarction, and a recommended biomarker in many clinical practice guidelines and consensus statements.
As research interest shifts from myocardial infarction to myocardial injury, high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I (hs-cTnI) assays receive increasing attention, which requires higher performance. 1) Lower limit of detection (LoD) and limit of quantitation (LoQ) enables detection of cTnI at lower concentrations and minor changes in myocardial injury; 2) The coefficient of variation (CV) is less than or equal to 10% in samples from healthy individuals at concentrations above the 99th percentile upper reference limit (URL). Such requirements ensure enhanced analytical precision, accuracy and reliability of test results.
The development and application of the rapid “rule-in” and “rule-out” algorithms based on hs-cTnI assays aim at rapid triage and early detection of cTn changes following myocardial injury. It improves the sensitivity of early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction (AMI), and minimizes the “blind spot”. cTn levels are measured at 0 hour (time of initial blood test) and 1 hour or 2 hours later. Ideally, hs-cTn assays can detect changes in concentrations as low as single-digit pg/mL, which ensures accuracy and precision at very low analyte concentrations, and provides reliable evidence for clinical decision-making.
The growing demand for high sensitivity presents unprecedented challenges to specificity. Many factors can significantly affect the precision of hs-cTnI assays, such as heterophile antibodies, phosphorylation/dephosphorylation and macrotroponin. In light of this, we have developed chimeric (human–mouse) antibodies and antibodies from a variety of species, such as rabbit, sheep and goat. By optimally pairing these antibodies, we have boosted the anti-interference performance, accuracy and reliability.
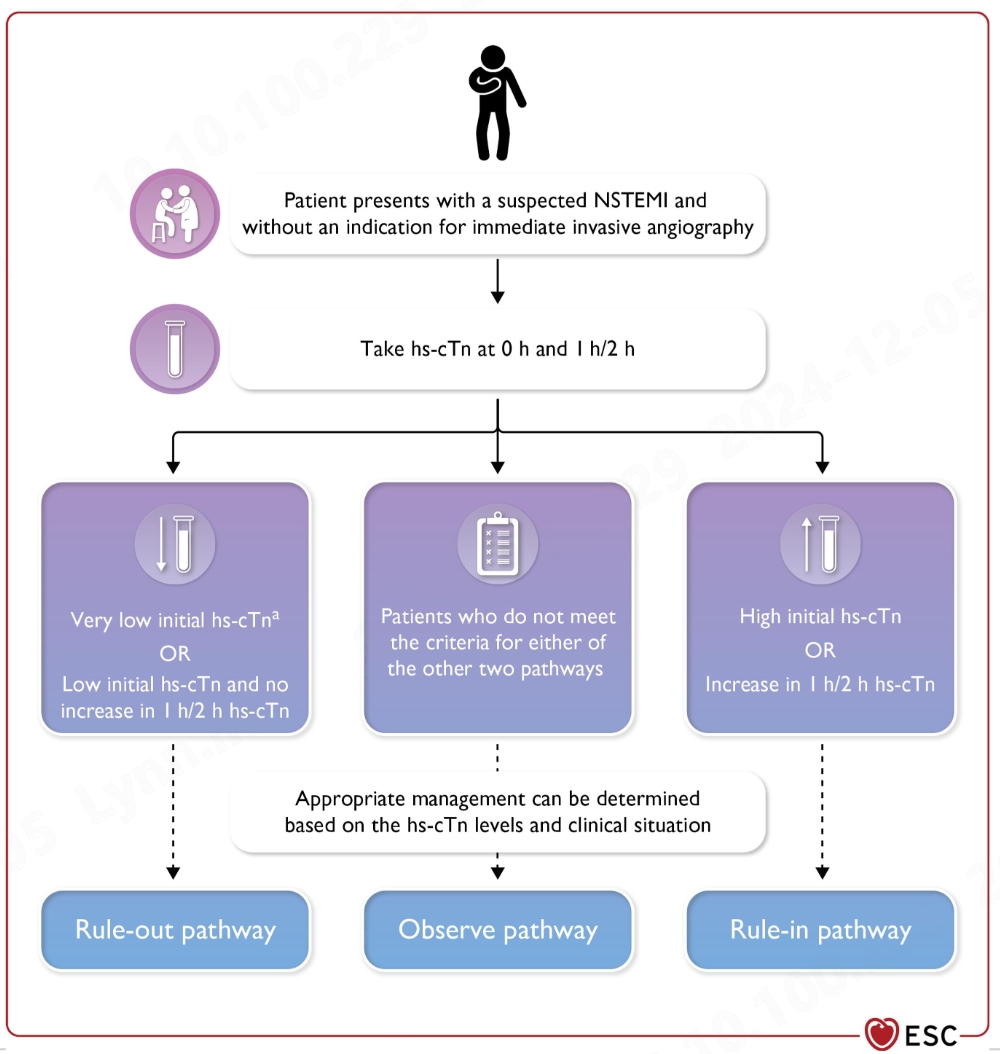
Source: 2023 ESC guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes (European Heart Journal;2023-doi:10.1093/eurhearti/ehad191)
Why choose us
1. Breakthrough in sensitivity
We have achieved a femtogram-scale breakthrough in the sensitivity of our new antibody pairs for hs-cTnI assays. They deliver world-leading performance in terms of limit of blank (LoB), LoD, LoQ and positive/negative (P/N) ratio, ensuring accuracy and precision at extremely low analyte concentrations.
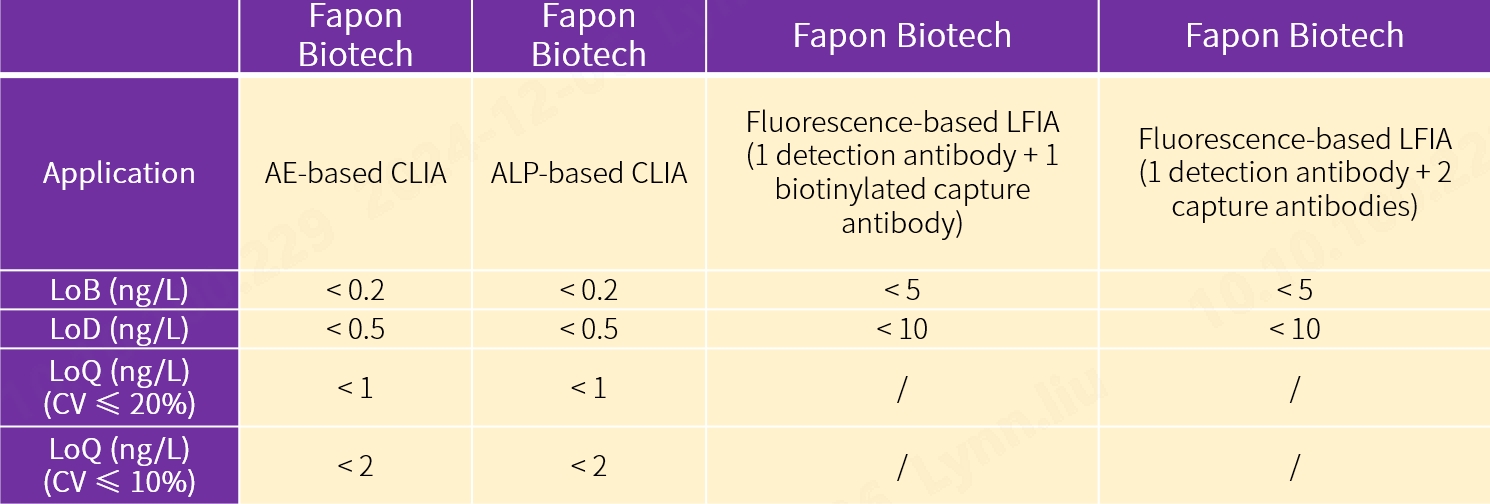
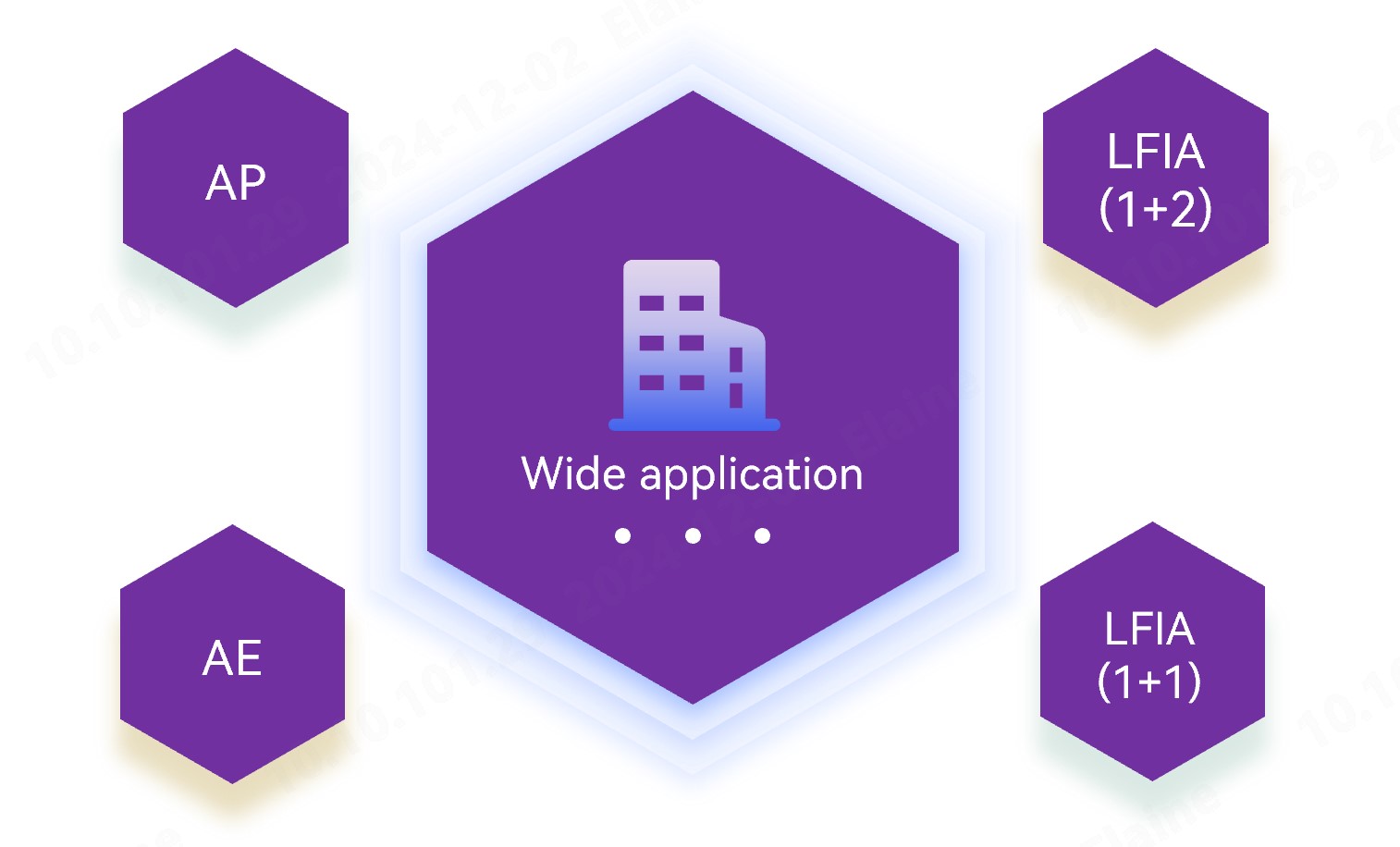
2. Wide application
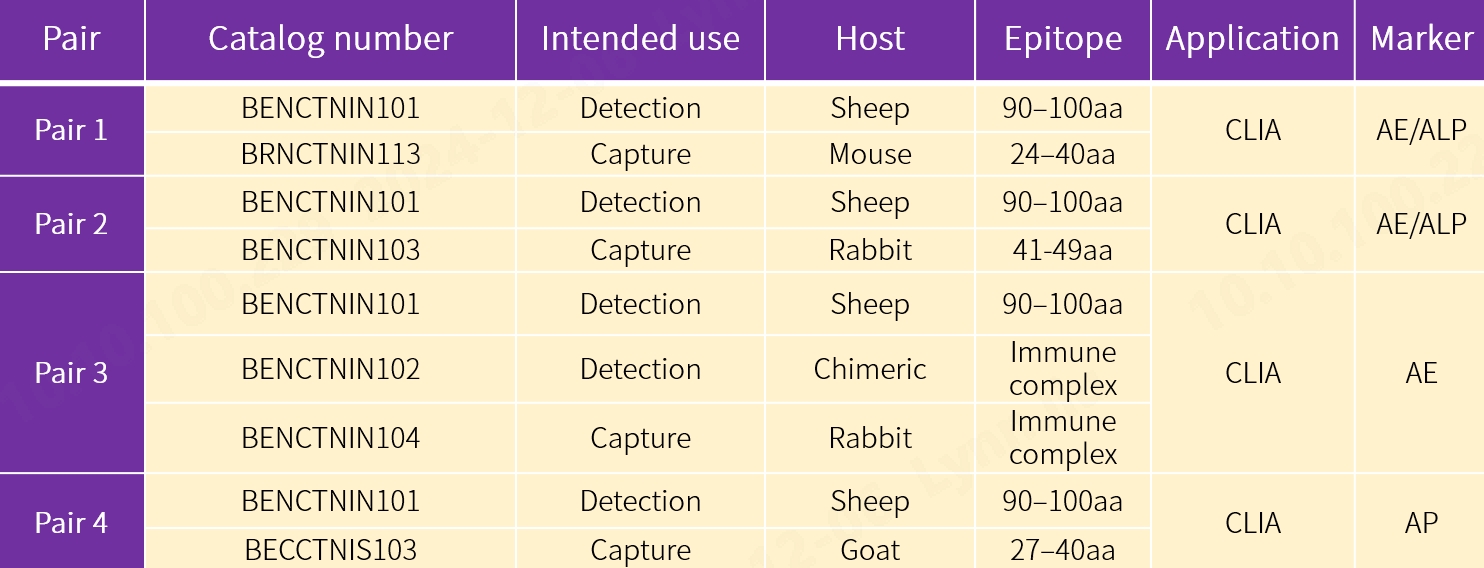
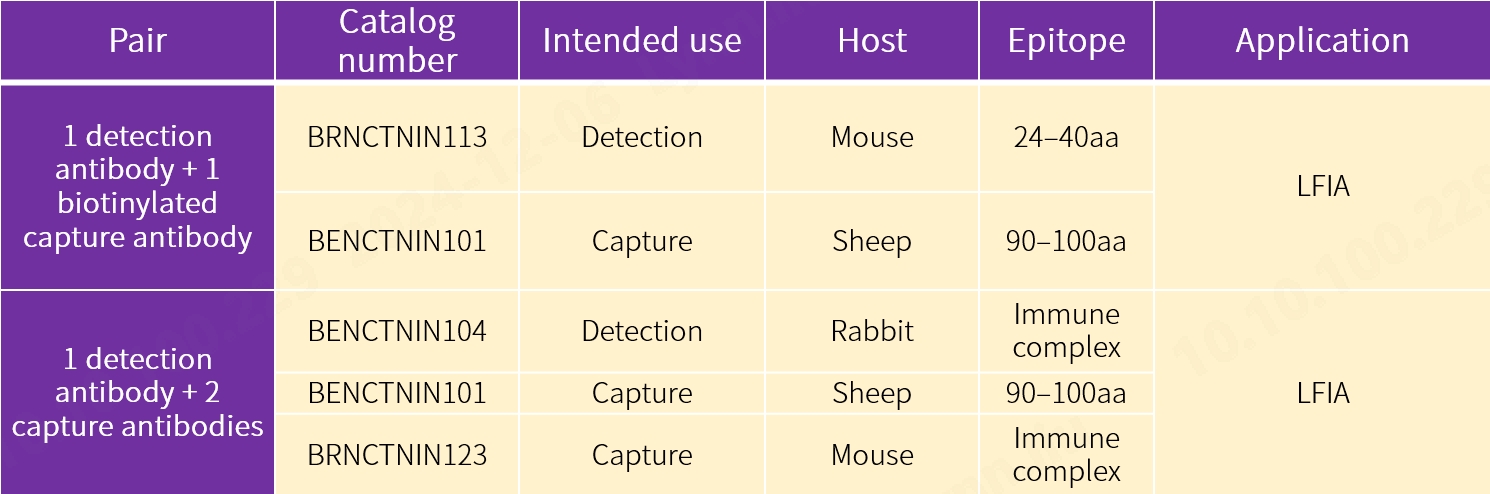
Our new antibody pairs are intended for use in chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) using acridinium ester (AE) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) markers respectively, fluorescence-based lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA) using 1 detection antibody and 2 capture antibodies, and fluorescence-based LFIA using 1 detection antibody and 1 biotinylated capture antibody. The performance proves to be exceptional.
3. Excellent anti-interference performance
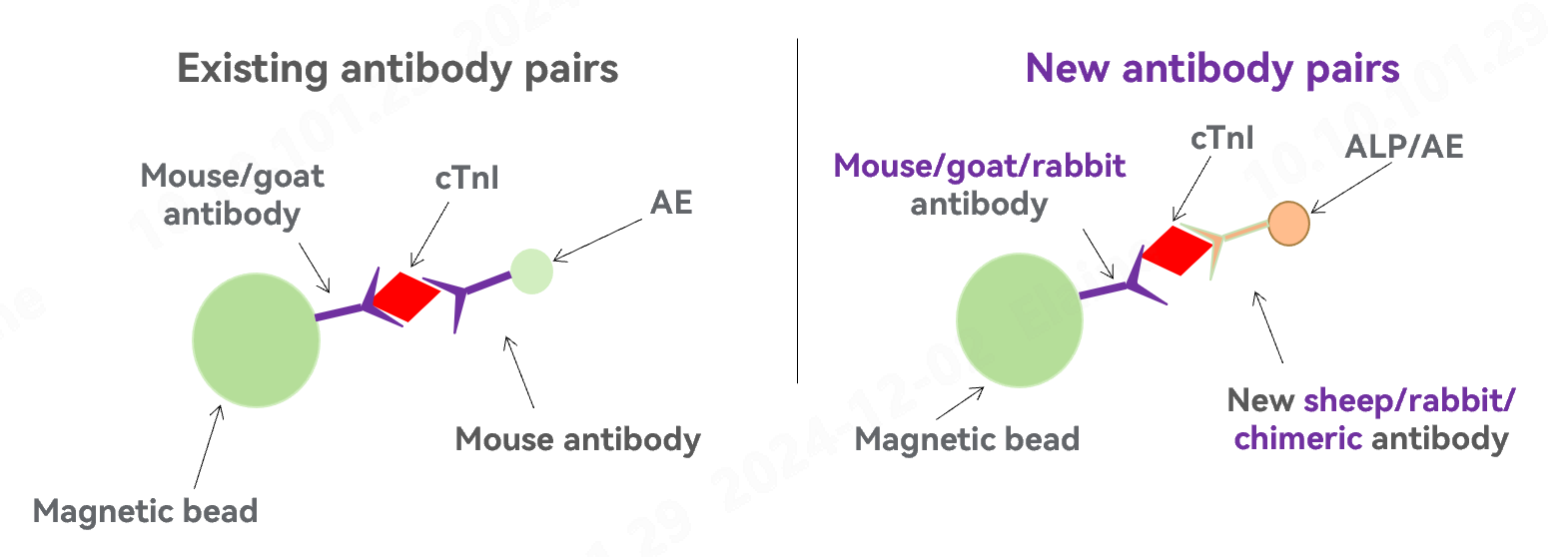
* Newly developed antibodies from sheep and rabbit deliver higher sensitivity.
* Optimal pairing among mouse, goat, sheep, rabbit and chimeric (human–mouse) antibodies significantly increases the anti-interference performance, and reduces false positives.
4. High correlation
Our new antibody pairs were compared to the hs-cTnI assays from a renowned IVD company. In AE- and ALP-based CLIA, and fluorescence-based LFIA using 1 detection antibody and 1 biotinylated capture antibody, the coefficient of determination (R²) was found to be extraordinary both within the linear range and at low analyte concentrations.
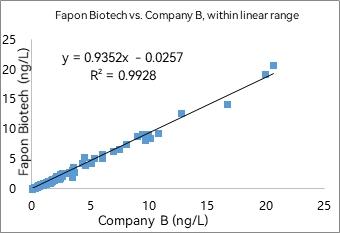
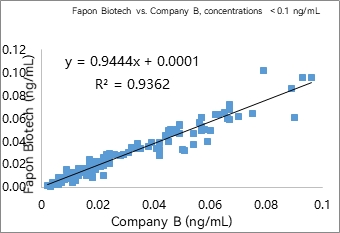
1) AE-based CLIA
R² was found to be 0.9928 within the linear range in 297 samples. R² was found to be 0.9362 at analyte concentrations < 0.1 ng/mL in 141 samples.
2) ALP-based CLIA
R² was found to be 0.9902 within the linear range in 297 samples. R² was found to be 0.9339 at analyte concentrations < 0.1 ng/mL in 141 samples.
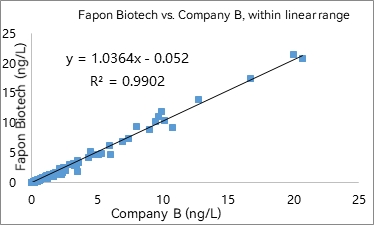
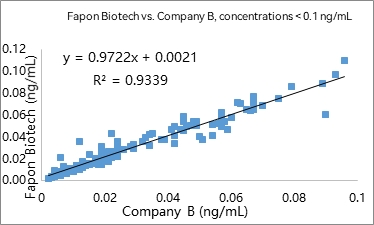
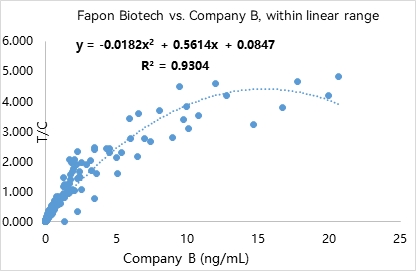
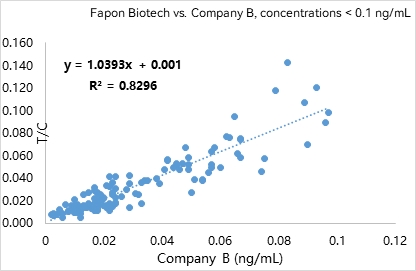
3) Fluorescence-based LFIA (1 detection antibody + 1 biotinylated capture antibody)
R² was found to be 0.9304 within the linear range in 309 samples. R² was found to be 0.8296 at analyte concentrations < 0.1 ng/mL in 130 samples.
Product list
1. New antibody pairs for CLIA
![]()
![]()
2. New antibody pairs for fluorescence-based LFIA
Coming soon
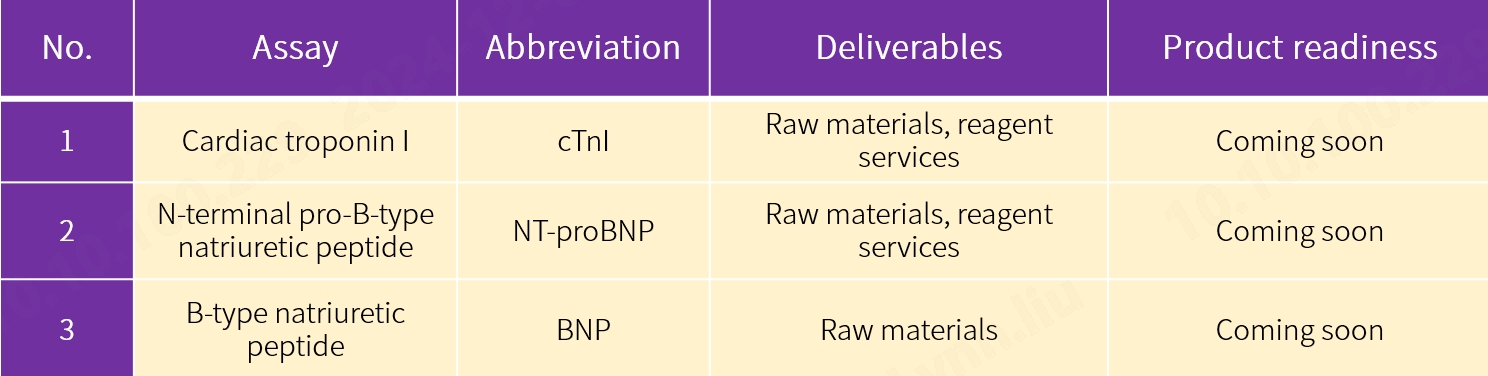
Our new antibody pairs for N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) assays are coming onto the market as well. We never stop innovating for specific applications in your lab. Choose from our comprehensive range of antigens, antibodies and enzymes, among others, for expedited assay development. Contact our sales team for more details.
References
[1] https://www.who.int/zh/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds)
[2] Vaduganathan M, Mensah G, Turco J, et al. The Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Dec, 80 (25) 2361–2371.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2022.11.005
[3] 胡盛寿,王增武.《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2022》概述[J].中国心血管病研究,2023,21(07):577-600.
[4] European Heart Journal;2023-doi:10.1093/eurhearti/ehad191
[5] High-Sensitivity-Cardiac-Troponin-I-and-T-Assay-Analytical-Characteristics-Designated-By-Manufacturer-v062024