Fapon Launches Groundbreaking Double Reagent Solution for Total Vitamin D in Human Whole Blood
Fapon has made a significant stride in the health sector with the release of the groundbreaking double reagent solution for the quantitative detection of Vitamin D in human whole blood, requiring only 5 μL of fingertip blood for the process.

Children and Vitamin D
Vitamin D is crucial for the growth and development of infants. It regulates calcium and phosphorus metabolism, promotes calcium absorption, and is an essential nutrient in children's bone development. Rapid growth in children makes them susceptible to deficiency. Vitamin D deficiency in children can lead to growth retardation and rickets.
Prolonged vitamin D deficiency can disrupt calcium and phosphorus absorption in children, hindering normal bone and tooth development. It can also lead to mental retardation and slower physical growth in children.
The primary sources of vitamin D for infants are breast milk, food, and sunshine. Breast milk is naturally low in vitamin D, and even with maternal supplementation, it is challenging to meet the daily needs of infants. Vitamin D, particularly VD2 (from plant sources) and VD3 (from animal sources), is mainly found in marine fish, animal liver, egg yolk, and butter, which are high in fat content. Vitamin D3, synthesized in the skin upon sunlight exposure, is the body's primary source of vitamin D, accounting for over 90% of the vitamin D required by the human body.
However, prolonged sun exposure can harm young children's skin and eyes, and children with limited sunlight or outdoor activities in winter and spring need additional vitamin D supplements. According to “Expert Consensus on Clinical Application of Vitamin A and Vitamin D in Children in China (2024)”, Moderate vitamin D supplementation is recommended for infants and young children:
Neonates: 400 ~ 800 U/d should be supplemented as soon as possible after birth to prevent rickets.
Premature infants, multiple fetuses and low birth weight infants: 800 U/d from 1 week after birth and 400 U/d after 3 months; Vitamin D 400 U/d if fed premature infants formula.
Children with recurrent respiratory tract infection, diarrhea, iron deficiency and malnutrition: 400 ~ 800 U/d.
The patients who met the diagnostic criteria of vitamin D deficiency rickets were treated with daily therapy or high-dose pulse therapy, mainly PO, the minimum therapeutic dose was 2000 U/d, and calcium supplementation was emphasized. The course of treatment was at least 3 months. After 3 months of treatment, serum 25 (OH) D was examined to evaluate the therapeutic response [1].
Excessive vitamin D intake can lead to hypercalcemia, nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, thirst, frequent urination, constipation or diarrhea, confusion, and fatigue. In children, it can lead to mental retardation, abnormal bone growth, irritability, and depression.
Therefore, vitamin D testing for infants and young children can prevent vitamin D deficiency or excessive supplementation, thus avoiding the occurrence of diseases.
Current Status of Vitamin D Detection in Children
The “Expert Consensus on the Clinical Application of Vitamin A and Vitamin D in Children in China”, which was discussed and formulated by the expert group of the child care Branch of the Chinese Preventive Medical Association in 2021, clearly defined the criteria and criteria for determining vitamin D deficiency, and emphasized that serum 25 (OH) D concentration ≥ 50 nmol/L (20 ng/mL) is considered normal. (Note: 1 ng/ml = 2.5 nmol/L)
The nutritional status of vitamin D is measured by serum 25 (OH) D. According to this, the 2022 Practice Guidelines for Clinical Problems Related to Vitamin D Nutrition for Children in China divides it into four levels:
Vitamin D deficiency: 25 (OH) D < 30 nmol/L, with an increased risk of developing nutritional rickets in this state for a long time
Vitamin D deficiency: 25 (OH) D 30-50 nmol/L
Adequate vitamin D: 25 (OH) D > 50 ~ 250 nmol/L, with 50-125 nmol/L being the appropriate level.
Vitamin D poisoning: 25 (OH) D > 250 nmol/L
Research indicates that vitamin D deficiency is nearly ubiquitous among Egyptian healthy adolescents (99%), with 94.8% having vitamin D deficiency and 4.2% having vitamin D insufficiency. Girls had a higher prevalence of vitamin D deficiency than boys. There was a significant association between lack of physical activity, sun exposure, and vitamin D deficiency [2].
Research in India also shows that there is a high proportion of children lacking vitamin D. In Indian scholars found that a majority (71%) of the children were Vitamin D insufficient with serum 25(OH)D concentrations between 50 and 74.9 nmol/L [3].
In Brazil, research has found that only 31·8 % of children were vitamin D sufficient (concentration <30 nmol/l and <50 nmol/l among 32·9 and 68·2 %, respectively) [4].
Fapon Launches Vitamin D Detection Reagent Solution for In Vitro Quantitative Determination of Total 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D in Human Whole Blood
Compared to the traditional method of detecting vitamin D in serum or plasma after blood centrifugation, fingertip blood detection is convenient and fast, requiring only a small amount of blood, a simple sampling process, no complex equipment, and rapid detection. It is almost painless: compared to venous blood drawing, fingertip blood drawing is less invasive and causes minimal discomfort, making it particularly suitable for infants and young children.
After one year's optimization, adaptation and clinical verification, Fapon officially launched the total vitamin D dual reagent solution for whole blood (venous blood) samples, which can easily complete precise and quantitative vitamin D diagnosis within 15 minutes with only 5 μL samples. The results are consistent with the chemiluminescence Immunoassay platform for the diagnosis of homologous serum samples. When used in conjunction with detection reagents for blood calcium, blood phosphorus, and blood alkaline phosphatase, it can achieve the goal of multi-item combined quantitative detection with minimal blood collection and bone metabolism in infants.
[Methodology]:
Latex immunoturbidimetry and double antibody method
[Reagent Formulation]:
Liquid double reagent, suitable for transmission and scattering analyzers, for convenient and rapid detection
[Reaction Parameters]:
Sample type: venous blood
Sample size: 5 μL
R1/R2: 320 μL /80 μL
Test time: 350 s
Detection wavelength: 650 nm
[Comparison of dosage forms]:
Fapon VD latex turbidimetric reagent, product number S5203, batch 20240717.
[Reagent performance]:
Each performance index is good, meeting the testing requirements of each laboratory.
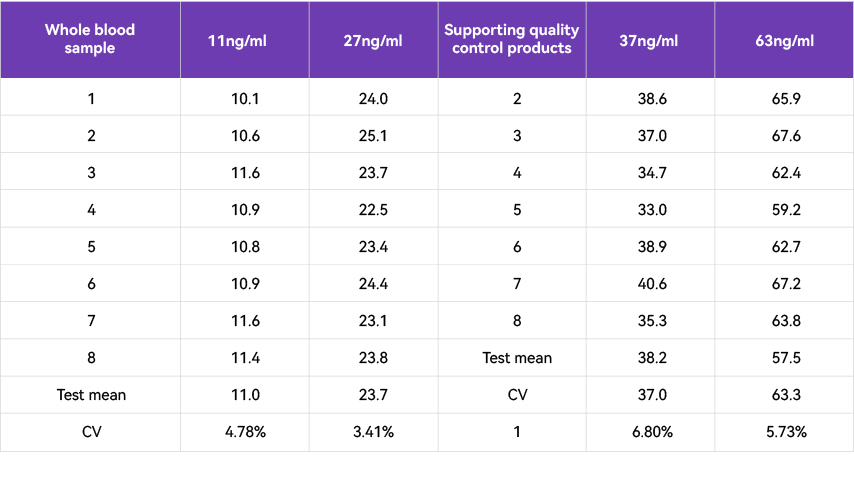
(1) The repeatability is excellent, and the linear range is controlled within 7 percent
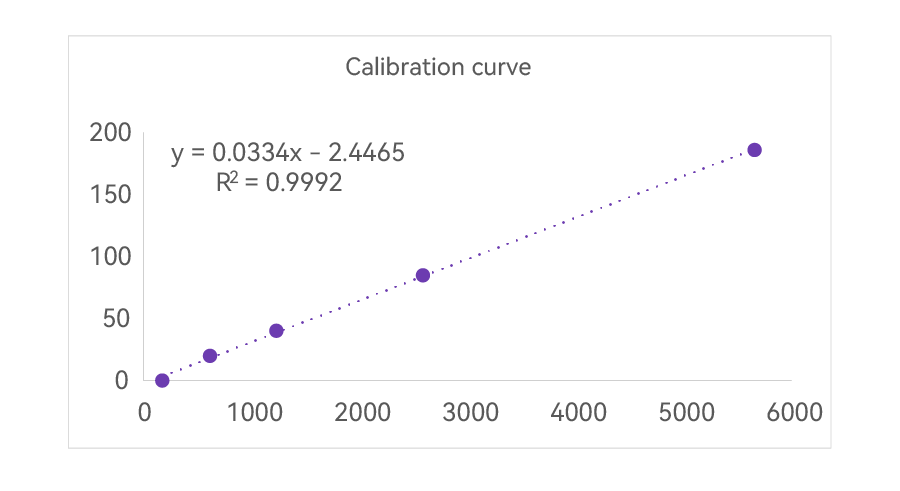
(2) The linearity is wide, reaching over 180 ng/mL.
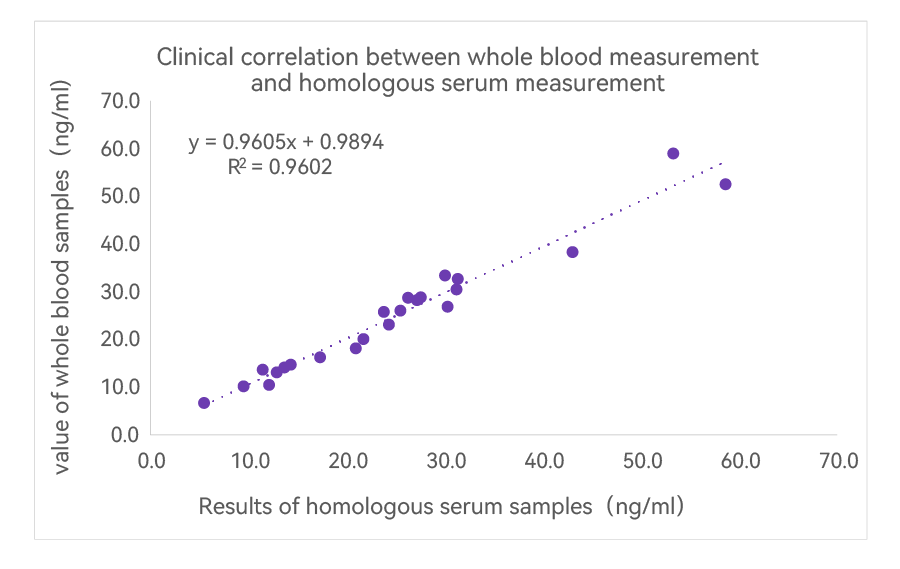
(3) Homologous serum samples tested showed high correlation over the full range (23 samples, values evenly distributed between 5-60 ng/mL, no sample rejection, no data modification, R2 > 0.96)
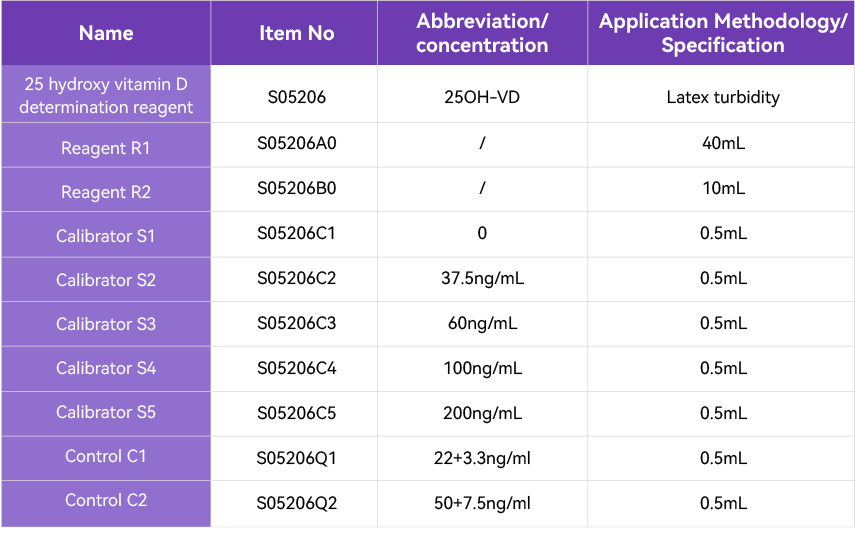
[Product Information]:
References
[1] child care Branch of Chinese Preventive Medicine Association. Expert Consensus on Clinical Application of Vitamin A and Vitamin D in Chinese Children (2024). Chinese Journal of child care 32.4 (2024): 349-358.
[2] Vitamin D status and healthy Egyptian adolescents. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Jul 23;100(29):e26661.
[3] Determinants of Vitamin D Status in Indian School-children. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Mar-Apr;22(2):244–248.
[4] Vitamin D sufficiency in young Brazilian children: associated factors and relationship with vitamin A corrected for inflammatory status. Public Health Nutr. 2019 Aug 23;23(7):1226–1235.